Key Vital Signs Tracked by Patient Monitor Devices for Comprehensive Healthcare Monitoring
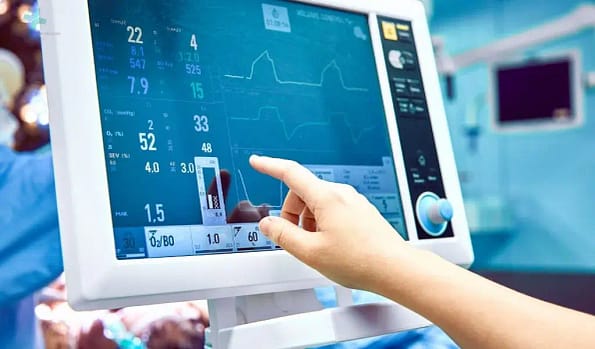
What vital signs can a patient monitor device track for comprehensive healthcare monitoring?
The Importance of Vital Signs in Healthcare
Patient monitor devices are pivotal in contemporary healthcare, offering a window into a patient’s well-being through the continuous tracking of vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate, body temperature, and oxygen saturation. These devices have evolved significantly from their inception, incorporating advanced features like carbon dioxide level monitoring, electrocardiogram readings, and non-invasive blood glucose monitoring.
They play a crucial role across various healthcare settings, from hospitals and clinics to home healthcare and emergency medical services, by providing real-time data that is essential for diagnosing, monitoring, and treating patients. With technological advancements, patient monitors have become more user-friendly, portable, and capable of supporting healthcare professionals in delivering prompt and accurate care. As we look towards the future, the integration of wearables, remote monitoring, artificial intelligence, and machine learning promises to further enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of patient care.
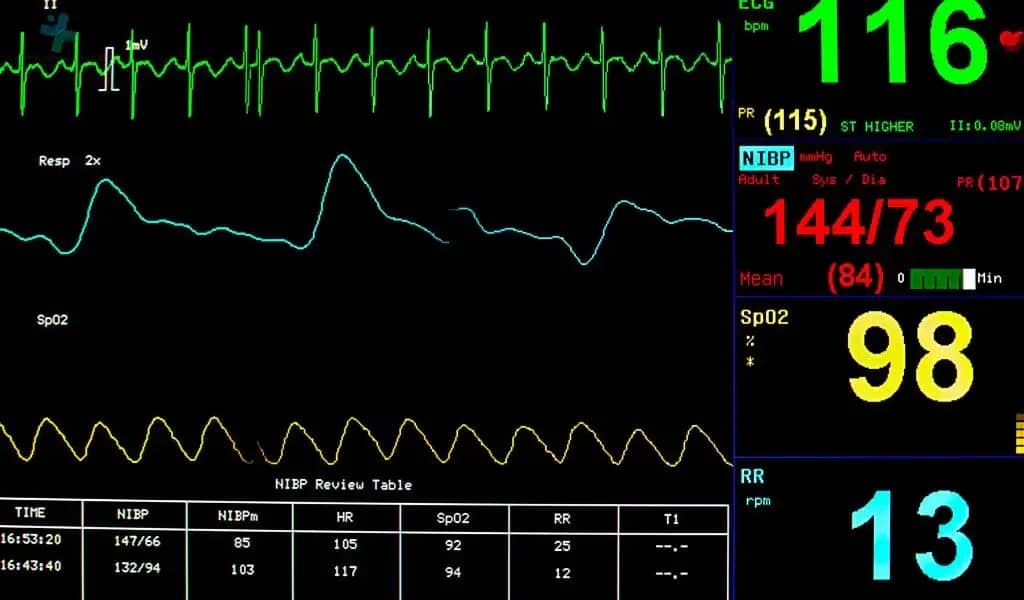
Core Vital Signs Tracked by Patient Monitors
Patient monitor devices are indispensable tools in the healthcare industry, meticulously designed to track a range of vital signs critical for comprehensive patient care. These devices enable healthcare professionals to assess a patient’s health status in real-time, providing essential data for informed decision-making and prompt intervention when necessary.
Heart Rate (HR): An essential indicator of cardiac health, HR monitoring involves understanding the beats per minute, which can signal various health conditions based on the rate and rhythm. Devices track HR to assess the heart’s performance and detect abnormalities early on. Techniques include electrocardiography and pulse oximetry, offering insights into the patient’s cardiovascular health.
Blood Pressure (BP): Monitoring BP is critical for detecting hypertension or hypotension, conditions that can lead to severe health complications if left unaddressed. Devices measure systolic and diastolic pressure, employing automated cuffs for regular assessments. This continuous monitoring is vital in managing chronic conditions and during surgical procedures.
Respiratory Rate (RR): RR, the number of breaths per minute, is a crucial measure of pulmonary function. Monitoring RR helps in identifying respiratory distress or failure early, crucial for patients with pulmonary conditions or under anesthesia. Methods include capnography and impedance pneumography, ensuring accurate and continuous observation.
Body Temperature: A fundamental vital sign, body temperature variations can indicate infections, inflammations, or other medical conditions. Patient monitors utilize various methods for measurement, including oral, rectal, and infrared thermometry, providing crucial data for diagnosing fevers or monitoring hypothermia.
Oxygen Saturation (SpO2): SpO2 monitoring assesses the oxygen levels in the blood, critical for patients with respiratory issues, undergoing surgery, or those on ventilatory support. Pulse oximetry is a non-invasive method used, offering real-time insights into the patient’s oxygenation status and ensuring timely intervention in case of hypoxemia.
Advanced Monitoring Features
Carbon Dioxide Levels (EtCO2)
EtCO2 monitoring is crucial for assessing a patient’s ventilatory status, providing insights into their respiratory function and metabolism. This feature helps detect hypoventilation or hyperventilation, guiding interventions in critical care and anesthesia management.
Electrocardiogram (ECG) Readings
ECG readings are vital for monitoring the heart’s electrical activity, identifying any irregularities in heart rhythm or structure. This feature is indispensable for diagnosing cardiac conditions, monitoring cardiac health, and guiding treatment plans.
Non-Invasive Blood Glucose Monitoring
Non-invasive blood glucose monitoring offers a revolutionary approach to diabetes management, allowing for continuous glucose level tracking without the need for frequent finger-prick tests. This feature enhances patient comfort, improves glycemic control, and can significantly impact diabetes management strategies.
Choosing the Right Patient Monitor for Your Healthcare Needs
Selecting the appropriate patient monitor is critical to ensuring effective healthcare delivery. This decision should be guided by several key factors to ensure the device meets the specific requirements of your healthcare setting and patient needs.
Factors to Consider
- Type of Healthcare Setting: The choice of patient monitor can vary significantly depending on the environment it will be used in, such as hospitals, clinics, or home healthcare. Each setting demands different features, from high-end monitors for intensive care units to more basic models for routine monitoring at home.
- Range of Vital Signs Needed: Determine which vital signs are most crucial for your patient population. While some settings may require comprehensive monitoring, including advanced features like EtCO2 and non-invasive blood glucose monitoring, others might only need to track basic vitals such as heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation.
- Ease of Use and Portability: For healthcare providers on the move or in-home care situations, ease of use and portability become paramount. Monitors should be user-friendly, with intuitive interfaces and lightweight designs to facilitate mobility and ensure timely patient care.
The Future of Patient Monitoring Technology
- Wearables and Remote Monitoring: The future points towards an increase in wearable devices and remote monitoring solutions, enabling continuous patient monitoring outside of traditional healthcare settings. This shift promises to improve patient engagement, reduce hospital readmissions, and facilitate early detection of potential health issues.
- AI and Machine Learning in Healthcare Monitoring: Artificial intelligence and machine learning are set to revolutionize patient monitoring by providing predictive analytics, personalized care plans, and automated alerts for abnormal vital signs. These technologies can enhance diagnostic accuracy, optimize treatment strategies, and significantly improve patient outcomes.
In conclusion, choosing the right patient monitor involves a careful assessment of your healthcare setting’s specific needs, the vital signs that are crucial for your patient care objectives, and the technological features that will most enhance your ability to provide effective monitoring. As patient monitoring technology continues to evolve, embracing innovations such as wearables, remote monitoring, AI, and machine learning will become increasingly important in delivering high-quality, patient-centered care.